Giuseppe Strappa,
TERRITORY IS ARCHITECTURE
(From: G.Strappa, P.Carlotti, A.Camiz, Morfologia urbana e tessuti storici. Il progetto contemporaneo dei centri minori del Lazio, Roma 2017)
1. INTRODUCTION
The research effort on the small towns of the Latium Region has had to take into account, as could easily be imagined, the general issues that have long been subjects for debate in the field of contemporary architecture, such as the concept of landscape, together with the more closely implicated notion of territory, whose technical and operational definition has proven to be of key importance to the work carried out in the field; and then the ideas of settlement and urban organism, equally important for arriving at an active, critical analysis of the settled zones in the area being studied; finally, the notions of specialisation and specialised building, indispensible to proposing a process for updating existing constructions, that can constitute an alternative to the immobile preservation of the historical heritage, with the resulting sprawl of new construction.
Indeed, as we will see, this study proposes the critical continuation of processes underway: not to abandon small historic towns to the role of “monument” that contemporary culture seems to have assigned to them, subjected to conservative restoration only, as if time had stood still. We believe that we need to understand how the processes of transformation and specialization, aggregation and “dequantification”, that have accompanied their history, must also be continued nowadays, accepting the obvious fact that an urban organism needs to undergo constant transformation in order to live. Unquestionably, these transformations must contend with the value of historical evidence and the artistic features these towns are able to boast, universally shared, and hence, proportionate and congruent.
This is the reason why any contemporary action must be related to the broader, surrounding environmental context, establishing a relationship of necessity with the site’s characters. It must be related to the natural setting that history has inserted it in, which, in all Italian regions, is always the product of transformations performed by man. In short, it must take into account the landscape it is located within which, therefore, becomes a primary purpose of the research.
Hence, some information is provided below regarding method for large-scale study of the problem examined during this investigation that formed the basis of the research on small towns in Lazio, starting from the notion of landscape and territory which represents a critical key choice.
2. TERRITORY IS ARCHITECTURE
One of the basic ideas that lies at the origin of the European landscape culture is most definitely of a literary and pictorial nature, linked to those anti-classical movements that put forward new aesthetic needs in Northern Europe during the mid-eighteenth century. New proposals springing from the appeal of categories difficult to define within the traditional notion of art, linked to intuition, rather than rational consciousness of things.
No longer beauty originating from rules, but aesthetic sentiment generated by experiences that cannot be investigated using reason. An overturning of aesthetic principles that will lead to one of the modern interpretations of landscape, the study of which is based on the form’s perceptual aspects, the consequences of which can still be seen. It is no coincidence that while summarizing the characteristics of this new awareness in A Philosophical Inquiry into the Origin of Our Ideas of the Sublime and Beautiful (1757), Edmund Burke supported the aesthetic value of emotions aroused by large dimensions, darkness and the abyss, undermining the traditional notions of balance and harmony that reigned over the formulation of the idea of beauty. Not too different, after all, from when Piranesi’s research was proposed in Rome. Following in the footsteps of Salvator Rosa from a century before, Piranesi turned to the artificial landscape of ruins around him to interpret messages, the text of which had been lost but fragments of which had remained to be freely reassembled and interpreted, like in Northern Europe where the focus was on the natural landscape, the dark forest and the stormy sea as a source of artistic renewal.
Some French and English paintings dating from last years of the eighteenth century, by Vernet and by Turner, offer confirmation that the new notion of landscape was due to interpretations that went beyond the pretty and pleasant, following the ideas aroused by deep caves, rugged peaks and summits and natural disasters. Mankind no longer grasped the friendly nature of classical literature’s beloved pastoral landscapes, but captured its disturbing aspect, “passing through the realm of demons and gods.”
The picturesque, the romantic notion of nature that generated a complete current of the European landscape, is the offspring of this upset of tradition that exalts the uneven and inconsistent, the asymmetrical and discordant: all that is different and hence worthy of being painted. The strictly architectural, design-related aim of such an attitude is clear. William Gilpin, the new aesthetics’ first theorist laid the foundations by stating that irregularity, which the picturesque is fundamentally linked to, is not so much a lack of order as the presence of a non-rational order. An order based on perception, on intuition, on compositional principles that cannot be demonstrated, on the exchange of emotional dyads that varied in accordance with the cultural climate and historical context. For the philosopher Edmund Burke, love and hate, attraction and repulsion, for the architect William Chambers, the revolting and the magical. But as far as all are concerned, the focus of research is nature, bent to a totally apparent randomness, designed with care, and not unspoilt nature, waiting to be contemplated.
The symptoms of this new awareness seemed to appear greatly in advance in Latium’s landscape, already in the mid-seventeenth century, favoured by the immeasurable combination of vegetation, buildings and ruins, as can be seen in the extraordinary painting by Pietro da Cortona depicting the Saxons of Furbara in the Tolfa mountains, a landscape of shadows where man appears lost and threatened by the harshness of the overlying ridges. Even minor landscape painting shows signs of an almost pre-Romantic attention given to Latium’s panoramas, such as, for example, the figure of the seventeenth-century painter Gaspard Dughet (1615-1675), born in Paliano to a French father, whose paintings feature radiant villages perched on ridges overlooking deep valleys dominated by dense vegetation and crossed by waterways. A new anxiousness that was not part of his master, Nicolas Poussin’s vision and which instead served as a foundation for a large amount of landscape art dedicated to Latium. For example, the numerous paintings where Gaspar van Wittel depicts the waterfalls in Tivoli, with the water breaking, violently, between buildings and vegetation, a vital flow amid the town’s sleepy panorama.

But ruins also appear as an inexplicable episode, as an evocation of the built world that emerges in the landscape (with rocky ridges and tuff hills) in a sort of exemplification of the architectural order where tall constructions, borne and artificial, emerge from the natural base, from the load-bearing, unspoilt rock.
A nature that envelops all and processes even the far-off echoes of the industrial revolution that in this area were to arrive above all through new paper mills, once again linked to the water and natural landscape. The paper mills of Grottaferrata from the early nineteenth century are shown as ancient castles and monasteries surrounded by vegetation in etchings by Charles G. A. Bourgeois.

It is clear how, even in the Latium of woods and traces of ancient times, the prevalence of the perceptive aspect on the rational and transmittable method led to the formation of a landscape tradition of Northern European origin. The latter linked, on the one hand, to the experience of landscape painters and, more generally, the visual arts and, on the other, to the experiences of landscape architecture where botanical interest and picturesque transformation of the natural soil prevails.
Indeed landscape means this “modelling of the earth”, with an emphasis on the natural aspect of the cognitive environment the term is associated with, as opposed to the term “paesaggio”, associated with the term “paese” and hence to the Latin pagus meaning village, acknowledging, in a concise manner, a relationship of solidarity between the land and human settlement.
Therefore, the landscape as a cultural expression is linked to the inhabited space, to the cooperation between natural and artificial resources, to the transformations that interpret the form of orographic peaks, valleys, plains and their ability to become a built environment. In short, it is the territory’s visible aspect, the concise expression of its structure.
This different way of observing the landscape, not only for aesthetic and contemplative purposes, but as a union between the natural land and man’s intentional transformation, with its own valuesand culture, is an architectural interpretation deeply rooted in the Mediterranean world and in its humanistic tradition. An interpretation, however, that found its first interpreters in the innovative environment of German geographers who were the first to introduce the notion of Kulturlandschaft, cultural landscape.
They raised the epistemological problem of how and with what means you were to look at the landscape by introducing a fundamental factor – time – into their study.Every landscape has meaning as a “historic landscape”, the result of a construction process that can be rigorously learnt, whose characteristics can be studied methodically.Alexander von Humbolt, a geognostic (he defined himself as such) from Berlin, had already laid the foundations, at the end of the eighteenth century, of study of the territory as a science whose point of departure was interpretation of the situation under investigation 1 in order to understand the relationships between things and obtain a summary of these. The change is clear: the noble and emotional observation of the artist looking at nature, in itself detached and neutral, was replaced by the study of the reality constructed by man starting from its nature, in itself political. A reality which, in order to be a human product and not an unalterable aspect of the problem, can be subjected to criticism, in the middle-class meaning of the innovative workability of knowledge. In other words designed. The human geography studied by Friedrich Ratzel and Otto Schlüter was already, to some extent, a “working interpretation”. It raised the problem of the processes of humanisation of the area2 , and subsequently that of cultural landscape 3, at the end of the nineteenth and the beginning of the twentieth centuries, defining the terms of a new discipline, which studies the landscape in terms of its shape, as an expression of territorial construction.
It is this tradition of learning which, in contemporary terms, gives birth to a new focus on relations between the city and the territory and on urban studies, promoted mainly by M.R.G. Conzen in England, where the geographer moved in 1933 from Nazi Germany.His all-important study of Alnwick 4 contains many of the premises to more advanced studies of urban morphology, put forward through the tangible interpretation of a small urban centre of medieval origin. While in Italy, active study of the territory 5 as a historically identified organism had one of the most original schools, founded by SaverioMuratori in the 50s.
The substantial similarity and complementarity between the wealth of knowledge of the English geographical school headed by M.R.G. Conzen and his successors, (J.W.R. Whitehand, T.R. Slater, P. Larkham, K.Kropf, and his son Michael Conzen) and the Italian school founded by Muratori, consisting mainly of architects that examine the formative processes of the city and territory, was acknowledged with setting-up of ISUF (International Seminar on Urban Form) in 1994. Above all they shared the belief that all forms of the territory and city are the result of a process, of the progressive, systematic association of parts, and that it makes sense to break it down and investigate its components only if we take into account its essential unity and indivisibility.
The foundations were laid for an interdisciplinary work, which this study is part of, through which geographers and architects could share a single field of studies, maintaining and intersecting method characteristics and interests.
3. MATTER AND MATERIAL OF THE TERRITORY
Territory is materia signata, a substance which man’s consciousness acknowledges as having an aptitude for transformation: dedicated material of an architecture in the most complete sense of the word.
Therefore, use of the natural matter, of the soil bed in its different, complementary meanings related to vegetal or geological world lies at the origin of the formation of the territory. So, its study is linked to the architectural interpretation of a process, to the problem of how matter becomes material before being transformed into a territorial element and how each element arising from this transformation contributes to the formation of a more general “territorial organism” comprising increasingly higher-level structures.
The territory insofar as a product of a common environment with its values, techniques, characteristics and culture springs from solidarity and cooperation between people and nature.
As an organism composed of structures modelled by the hand of man from a natural soil, it must be defined as a construction, and should be interpreted as such.
The same etymological derivation of the word indicates the notion of dwelling place, subsequently built and rebuilt by its inhabitants that establish a close relationship with the land: a territory belongs to a community of people but they also belong to the territory.The house itself, a concise demonstration of ways of sharing space, expresses this involvement through the idea of “appurtenance”. Not only does appurtenance (from per-tinere) indicate the legal concept of possession, but, as we shall try to show, also the notion of a physical link that connects a building to the area on which it stands, then one building to another and then these buildings to the routes in order to form fabrics.
Therefore, the notion of appurtenance is the basis on which synthesis between the different scales is founded.
The very idea of territory comes from the link between the notion of natural land and that of artificial transformation made by man during human settlement, of transformation and adaptation of the land to living requirements. This process is usually interpreted as comprising a succession of changes punctuated by periods of momentary equilibrium, offering a reasonable idea of a historical sequence actually formed of an ongoing flow of change and upheavals.
Indeed, the historical-processual meaning of an urban organism or system of routes cannot be understood unless we place their formation within a relationship of necessity with relations with the territorial surroundings established over time and space. So, the term “landscape” will be used to refer to the man-made form of the territory, in other words the visible aspect of a structure of relations that brings together in the notion of organism, the various scales of buildings and the natural environment, always transformed by the hand of man in various ways and to differing extents.
The territory is also a civil heritage, a wealth recording the sequence of cultural choices (the selection of route models, building types, forms of production) carried out by the people that settled therein. Therefore, any action at this level requires understanding of the characteristics that can be seen in the territory through the form, remembering that this is the recognisable outcome of a process in progress: transformation of natural land into civilian land through subsequent phases of human activity.
It can be interpreted as a set of cooperating parts, in other words a set of territorial elements, settlement structures, production systems linked by ever-changing relations of need. So, it can be looked on as an organism. And just as in all built organisms, the civil phases and cycles determining its formation, transformation, fragmentation and ruins can be recognised therein.
Therefore, the notion of territorial organism as a dwelling place comprising parts that cooperate with each other (routes, settlements, production areas) is a complex one that summarizes the processes that take place at all minor levels: building organism, aggregative organism and urban organism.
Each territorial organism has its own, unique and unrepeatable characteristics, originates and transforms itself in accordance with specific processes, diversified over time and space. Nevertheless, each one shares some typical characteristics with the others, resulting from a human process that, inevitably, has some affinities with other processes. So we will refer to the shared, general nature of a territory as a wealth of processually-inherited physical characteristics common to a historical and geographical situation. These are combined with the set of notions and common settlement choices that determine operations to transform the original natural setting – the matter of the process in the conditions preceding all human action – into an inhabited location.
A typical behaviour that is “identified” (takes on unique, unrepeatable, individual characteristics) in the real transformations of the land determined in space and time, according to the predispositions of the subject matter (oro-hydrographic system, geological nature of soil etc.) and the purposes of the subject matter. In other words, in relation to a specific geographical area and a given historical and civil period.
The concept of “general nature” can be used to recognize the greater or lower level of organic unity of an area, which can comprise parts closely linked in a relationship of necessity, perfectly proportioned and congruent one with another, but may also comprise relatively autonomous and serial elements, which are organized by a less binding, formative and dislocative order.
As with the transformation of matter into material, the first and most basic of architectural processes, even the most complex phenomenon of transforming the natural land into inhabited land is related to choices made by a process split into two critical phases.
The first phase comprising distinction and selection, comes from awareness of the difference between things and recognition of their suitability to be used and transformed in order to form a territorial element. Distinction, the recognition of characters and selection, the choice of the most suitable among these, are intended, at this level, as identification of the predisposition of an area to be traversed and subsequently adapted for settlement before being transformed for residential and/or production purposes. This phase can be identified as “logical” through which the different possibilities of the component elements to be used are evaluated, subsequent to possible changes (not necessarily required).
The second phase, qualification and specialization (from species, indicating membership, the transition from comprehensive to specific) comprises limitation and transformation of the general characteristics of the matter (the natural land) to make them specific and suitable for particular purposes. It originates from identification of the relationship of complementarity and necessity among things. Qualification and specialization is meant as an “economic” transformation of the land in accordance with the specific roles it is expected to play within the territorial organism.
Routes are the result of a selection process through which the characteristics of the land (the form) and its suitability to be traversed are identified; followed by a process of specialization through which they take on different conformations and hierarchies in relation to the relationship established with the whole territory. From this viewpoint, the very act of building, the finalised transformation of matter, can be interpreted as a specialised modification of a part of the territory, a specific technical and economic phase within the human settlement process: individual finalisation to be followed by collective finalisation and organic synthesis. The fact that this synthesis has been lost in the contemporary situation should be cause for reflection, not simply an observation.
4. CULTURE OF THE TERRITORY
Settlement, therefore. represents a sort of reading of the natural soil performed by man, of its morphological and geological characters, of its susceptibility to be inhabited, linked to production areas that allow for life and development. This interpretation is the result of an experience brought about through the displacements that result in routes that become consolidated over time.
This is why, from a logical, as well as historical viewpoint, the territory should be interpreted in the basic diachronicity of its elements, acknowledging how the relationship of complementarity that is created between the component parts is the result of a formative architectural design and how its structuring is fundamentally linked to the dynamics of movements across the land, the potential and resources of which are “interpreted”.
Consequently, the formation and transformation of the territorial structure can be interpreted through a preliminary, necessary dyad of opposing and complementary terms: routes, where movement occurs, and settlements, where stopping occurs, connected with the life on the land that takes place permanently.
The choice of these routes, is made according to constant criteria within a certain phase of human settlement of the territory, for which one can refer to the typicality of routes in relation to the form of the land, as well as, in the same way, we can speak of typical forms of settlement related to the different forms of recognition of a place. The place goes from being general to “individual”, identified through man’s awareness of the specific characteristics that make that portion of territory unique and unrepeatable.
Therefore, technically speaking, settlement can also be defined as a temporary or permanent structure served by routes and formed of dwellings organically connected with complementary production area.
In the earliest forms of permanent settlements, linked to primitive forms of cultivation or rearing, the notion of “dwelling” expresses both, the idea of persistence in a (from de-morarimeaning to dwell) and that of permanent ownership.
This concept of ownership of a portion of the land originally comes from appropriation generated by work that is carried out in an ongoing manner, by the need, including “architectural”, to protect goods produced.
This is exactly the reason why early forms of appurtenances are usually associated with the anthropic transformations of the Neolithic age, when the spread of cereal crops generated a new relationship of organic solidarity between man and the land, making it possible to overcome the precariousness of random harvests.
Nevertheless, anthropic transformations that give rise to relatively stable structures, namely the decisive union of the natural land with the structures built by man to use it, belong to those historical phases and cultural areas where the need for constant maintenance of the land led to intense practice of all human activities and areas available, as in territories where working conditions had to be created through permanent irrigation systems requiring both systematic cooperation between artificial and natural land works, and organizational cooperation and specialization between working groups within the farming community. In this regard, we can see the case studies of structures already created in the earliest Neolithic period, in the flood plain of the Tigris and Euphrates that were forerunners of evolution of the territorial system of the Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian civilisations.
By implying changes of natural conditions not only encountered, but chosen by man, not only does this phase involve a decision regarding the land’s predisposition for settlement, but also awareness of belonging to the community that works the land, with a cultural transition comprising successive levels of semi-sedentism6.
The fundamental notion of enclosure, with the dual task of protecting and containing, which the origin of the Mediterranean city is based on, fits into the transition to more sedentary forms of work, associated with that of appurtenance 7.
The cities of Latium, as we shall see, are born from successive perimeters which became hierarchical in space and time: from the agriculture fence to the perimeter of the courtyard house, to specialist courtyard buildings, to the construction of the city walls.
Some of the relationships between the physical components that tend to establish a systematic relationship among themselves, have a structuring value and relative interpretation is of specific value for architects.
Such as relations linked to production. In the past this relationship linked settlements, farming and breeding with the integration between production cycles. A continuous cycle generating a close link between, for example, production systems and the land developed with fertilisation of the land connected to the production of fodder for rearing. A link that became complex in modern times, but which could still be interpreted processually, even after the start of the industrial revolution.
Or relations related to land ownership, for which real “land organisms” can be identified when the use of land available to the community integrated within private estates was established and regulated.
Therefore, if looked on as an organism, in accordance with the general given definition, the territory comprises sets of systems acknowledged as rivals for the same purpose.
From what has been briefly outlined, it follows that, as a first approach, the system of routes followed by the closely related system of settlements must be taken into consideration in order to understand its formation process.
Once the general organisation has been studied, the focus will shift to the system of dividing landholdings and the closely-related system of the use of natural resources (agricultural and manufacturing areas) or production system, which became permanent in a historically-later phase of the process of human settlement of the territory.
Systems, all of which conform to playing connection, housing and production roles, inextricably linked not only with each other, but to the land’s existing forms by systematic relations. A natural promontory, separated by two ridges, is the first environment in which man recognizes specific characteristics, finds an identity amid the group and natural land just as, at a later stage, a catchment area, isolated by orographic borders that are difficult to cross over, represents the location for development of a relatively homogeneous cultural area thanks to the ease of the internal trade it makes possible.
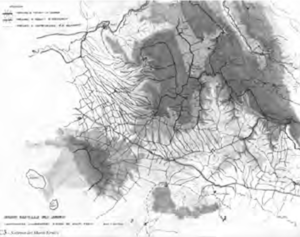
In this regard, we can observe the permanence of forms due to ridge routes that existed in Latium’s urban centres such as those illustrated herein, Jenne or Piglio, clearly generated by a process where the displacement of the population is from the main ridge to the secondary one in an orographic promontory suitable for defence and settlement. It should be noted how ridge settlements represent an anthropic constant throughout the whole history of the Latium territory, through to the contemporary period. Small settlements of single-family dwellings, sometimes built on illegal lots, are arranged along the mountain watershed in not such a different way as the older settlements. The very clear case of the recent expansions in Olevano Romano are detailed herein.
The relationship of complementarity between the route structure and form of settlements is clear in all these cases. Routes and settlements create a recognizable, even if not autonomous subsystem within the territorial organism in the same way in which agricultural lands and manufacturing facilities form a single subsystem. This is why, we consider it legitimate in the study presented herein, albeit with due caution, to examine the first of these dyads which makes it possible to interpret the territory in the form that we have inherited, as a result of the architectural process of ongoing transformation 8.
5. ARCHITECTURE OF ROUTES
If the territory is architecture, its study, as for any architectural structure, based on the observations set forth, cannot be separated from study of its construction transmitted by concise representation of its elements, structures and systems.
Territory, which we did not have an overall perception of through sight, has always been represented symbolically through abstractions throughout history, unless in recent times. Cartography, the instrument used for this representation, is the outcome of critical interpretation that provides the description of a piece of territory, concise and transmittable summary of the notions inferred from observation.
The symbol (from the Indo-European term symballein meaning to unite, put together), in turn, is the concise expression of a set of notions considered to be fundamental: therefore, it is itself the result of a choice and selection. This is why the cartographic instrument (the symbols and structures that link symbols one to another) is directly related to the interpretation the author has expressed of the territory represented within a cultural area and specific historical period.
Just as the lines of a process of transformation of the territory can be marked out, so the lines of a process of transformation of cartographic instruments can be marked out. This testifies to changes of the territory’s characteristics and, also, to the knowledge and awareness that man has always had of his own constructed environment over time and within various civil surroundings.
The Tabula Peutingeriana in particular contains a structure of routes; terrestrial routes are virtually absent in Giovanni Magini’s Atlas of Italy (1620); the road network prevails over the representation of other observable data on the territory in modern car maps; lastly, an underground map, in a gradual process of abstraction, is above all the mental and symbolic design of a network, not related to the physical form of the routes, with the real dimensions of the distances between the connected hubs. Therefore, for people such as architects, who need to interpret the territory in an active way, whose goal is intervention, it is essential to extract and interpret available information in a coherent manner, understanding that each representation is subject to interpretation since neither the territory’s history nor the contemporary situation can be shown objectively.
This interpretation is the link between subject and object in reading of the territory: between what the architect looks for through cartographic representation (linked to his own notion of territory and for the purpose of reading) and what the different maps, linked to the author’s notion of territory and the purpose of the representation, can offer.
A reading that can only proceed in phases related to human uses of the territory, starting from identification of the elements that are the first to structure the form of the territory, from routes and the way in which they are formed, consolidated, organised, specialised and hierarchised among themselves in a cooperative mutually-dependent way, in a congruent and proportionate manner with the settlements they link to.
The dynamic aspect of life that takes place on the land, the marks left by movement (displacements, crossings, migration) precede any other marks: any structure linked to a stop or a stay is inevitably associated with the routes that allow its existence.
Just like each element of the constructed environment, even routes have their typical characteristic. They can be recognized through common qualities that identify the historical period they belong to and at an areal level, pertinence to the culture of the populations and characteristics of the land that give them shape.
A preliminary, intuitive distinction between typical routes can be made through the hierarchy of the task they perform, and then through the route’s polarisations with the definition of scale:
– local routes, internal to each area or between border areas, polarized by settlements and urban cores;
– territorial routes originally generated by migration and, later, by links between areas of greater polarization (motorway routes provide a contemporary example);
– land routes, linked to the scale of production areas;
– urban routes, internal connections to urban areas.
But a more useful distinction for understanding formative processes certainly refers to their permanence over time, the “resistance” of routes, their plastic capacity to adapt to changes and needs, linked to the hierarchy of use and formative stages.
Roads created by the sole act of travelling along them, and paths formed through the repeated transition of cattle (or mule tracks) are, from this point of view, certainly the most basic and spontaneous ways of communication 9.
Tracks, marked out solely by the passage of people and animals over long distances, polarized by settlements, represent the corresponding road on a larger scale which is territorial. Despite the fact that some tracks (“pista in Italian” from the Latin pesta meaning “track”, “footprint”) resist over time, they are, by their nature, an unstable type of route, not consolidated by structures other than those for temporary shelter. Caravan routes directly linking two urban settlements 10 are a perfect example of this, often featuring specialist facilities such as caravanserais, arranged like stops on a day’s march.The formative principle that generates the caravanserai is, in some way, opposed that of the road which goes towards structuring of the territory, generating and hierarchising human settlements. Proof of this can be seen in the almost complete replacement by Turkish conquerors, of the Roman-Byzantine Anatolian road network comprising caravan routes that did not reuse the ancient military and trade routes, even if still in good condition, with caravan routes directly linking major cities 11.
Apennine sheep tracks (“tratturi” in Italian, from the Latin trahere, meaning to carry, to lead)provide an example of the modern-day permanence of routes of this type, paths formed through migratory movement of flocks that represented important roads at a territorial level until the beginning of the 20th century.
On the contrary, the term “road” (“strada” in Italian, from strata, meaning road in the sense of a paved road) contains the idea of permanence, of a stabilised route, of construction which requires planning and a design.
The same etymology of the more recent terms such as “cart track”, “carriageway “, “railway” and “motorway” testifies to their nature of specialist route.
Some typical stable routes can be distinctly read in the structuring of the Italian territory, especially in the central area, along the Apennines. They are the expression of both a logical sequence and a historical sequence.
Ridge routes are formed along the line of the watershed dividing two basins, often already the site of an early, random track. They represent continuous crossing on a territorial level connecting remote and extremely diverse areas. This reason why, as Fernand Braudel also affirmed, civilization evolves from the mountain to the sea, contrary to what our “plain land civilisation” would lead us to believe, can indeed be found in the original formation of ridge routes. “What are the causes?” – Braudel writes – Undoubtedly the variety of mountain resources; but also the rifeness of stagnant water and malaria in the plains; or uncertain wandering in those river areas. The plains inhabited nowadays, synonymous with prosperity, were later creations, achieved after centuries of collective efforts”12
They represent the deep-rooted structure of a territory that forms before others, due to the extension of the links they generate, the possibility they offer, in the early stages of construction, to move into regions still not settled by humans, following the highest geometric line and the prerogative to avoid travel through flat valleys. Indeed, these are often marshy and more difficult to cross over due to the necessity to pass through fords and crossing places. They are hierachised in accordance with various forms and depending on the form and importance of the orographic system the ridge routes are associated with.
The main ridge routes, which run along the highest mountain ranges and represent the natural location for territorial migration and penetration due to their extension, are formed where a more ongoing watershed can be used.
The main ridge routes in central-southern Italy, travelled along solely for north-south displacements, were already formed in the Copper Age and the Bronze Age, and comprise watersheds of the Apennines, the natural location for the migratory flows of the Italic populations. We can find a higher Italic ridge towards the Adriatic coast, and a less continuous lower Etruscan ridge towards the Tyrrhenian coast.
The secondary ridge routes, possible travel routes along which settlements can be built, are formed along the watersheds that branch off from the main ridge, providing access to the headlands that branch out, overlooking valleys through secondary promontories. Series of secondary ridges are evident in central Italy which, starting from the Italic ridge, head towards the Adriatic coast in close succession, and those which start from the Etruscan ridge toward the Tyrrhenian coast in a more distanced succession converging at times in route hubs that will become the locations for new, important urban organisms.
Infinite variants of this important aspect of the formative process of territorial structures can be found in the different hydrographic and orographic conditions of the territory of central and southern Italy.
A systematic vocation of the Tyrrhenian coast corresponds to a marked serial nature of the Adriatic coast of the Apennines where a regular and almost “modular” settlement structure corresponds to the almost regular series of promontories heading towards the coast. The Tyrrhenian coast where, for example, the ridges that branch off from the main Apennine ridge, namely the Latin and Sabine ridges, intersect with the Etruscan one from the north-west, at the ford on the River Tiber facilitated by the presence of the Tiber Island. It is here that the synechism of centres founded amid the hills by populations that had established themselves along the various ridges, was to give rise to the city of Rome.
The local counter-ridge routes replace the main ridge route in some sections and are located almost parallel to them. Therefore, they form as “short cuts”, on the high-altitude contour lines combining nodal points of the secondary ridge routes. They originated from trading needs and not only do they presuppose a basic structure of stable settlements, but also an early form of production specialization that makes trade necessary.
The continuous counter-ridge routes tend to fully replace the main ridge routes for long sections. Generated mainly by the trading needs of production areas, contour lines are formed at low altitude creating widespread routes connecting settlements.
Lastly, the synthetic counter-ridge routes are produced by two ridges with a ford in the middle, often representing a short cut to the main ridge.
Complementary to the ridge routes, the valley floor routes follow the orographic system’s thalweg, running alongside waterways, on the edge of alluvial areas. These routes are generally subsequent to ridge routes and single out long phases of equilibrium in the transformation of the territory, as during the large-scale planned agricultural structuring of the Roman period. Indeed, they are formed at the end of the process of installation of the territorial organism, or are the result of internal colonization that starts with landings, often settled at the mouth of rivers and connected by a system of coastal routes, representing, dynamic structures within major historical cycles, definitely less permanent than the corresponding ridge structures, requiring the occupation of plains and continuity in hydrographic structures. If we are to represent schematically an actually very complex hierarchisation of routes, three different types of valley floor routes can be identified.
The main valley floor routes do not actually follow the exact thalweg. Just as the ridge routes do not often strictly follow the watershed because of the natural difficulties that may be incurred travelling along it (peaks, walls etc.), but adapt to it through link paths. So, the valley floor route cannot occupy the space immediately adjacent to waterways, but are more often placed behind it, adapting to the edges of the flood areas, using the land’s systems of low hills or following the plains’ margins.
Thus piedmont paths are formed that are often complementary to the main valley floor routes.
The secondary valley floor routes often originate from the foothills and run close to the thalwegs of the valleys located between two headlands, proving to be complementary to the secondary ridge routes. These routes play an important role in linking water basins, reaching the passes in between them.
In the case study looked at herein, we can see the ridge routes connecting the towns of Cave, Pisoniano, Gerano, Rocca Santo Stefano, Bellegra and Olevano with branches that give rise to the promontory settlements of San Vito Romano and Genazzano, with the piedmont link of National Road 155 and the valley floor routes on a territorial level comprising firstly Via Casilina, followed by the Rome-Naples motorway.
6. ARCHITECTURE OF SETTLEMENTS
While routes provide a representation of movement, the flows of transit that read and hierarchise the form of the land, the second key component of the territory’s architecture is due to stopping, or the need to organize stable forms of solidarity between man and places suitable to be lived in
In the typically historical form, especially in central Italy, the structuring of settlements originates from the highest altitudes of the secondary ridges where the spring lines are encountered coming from the main routes, hence the possibility of permanent settlement, continuing in the direction of the valleys where the routes blend together into an organic structure with complementary settlements that form around fords (and at landing places along the coasts).
The descent towards the valley and the progressive specialization of production generates the need for trade and relative routes. This is the reason why, as already mentioned, settlements and routes are diachronic moments of a single process.
Therefore, the settlements at high altitude, are the first to form on secondary ridges that branch off from the main ridge used for major crossings and along which it is difficult to organise forms of permanent occupation due to the lack of water resources. While resources are available near the semi-permeable geological layers at the altitude where the spring line forms.
These settlements at high altitude, or high promontory settlements, represent the first permanent form of occupation of the land, followed by settlements and cultivated areas that tend to occupy the complete secondary elevation through to the valley head. The low promontory settlements, at the head of the ridges, firstly represent territorial hubs, albeit on a reduced scale, constituting the terminus (and therefore polarization) of a route, and subsequently, proto-urban centres 13, exchange nodes (through the formation of route hubs) with the valley, at the start of the phase of occupation and structuring of the plains, often originally marshland, and subsequently reclaimed.
Valley floor settlements are formed here, especially at the confluence of routes near fords, preferably, for obvious reasons, before the bifurcation of the rivers, from which additional proto-urban centres develop (for the market role taken on by territorial nodality) and real urban centres as such in the event of major polarity.
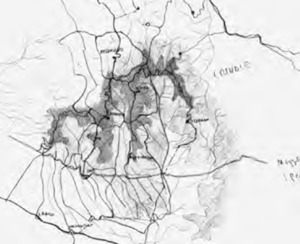
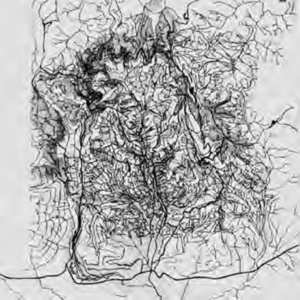
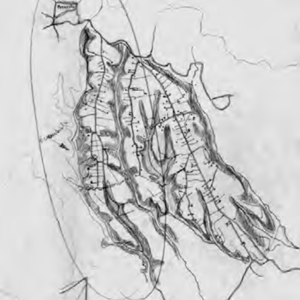
The graphic interpretations of the structure of routes and settlements in the study area performed by SaverioMuratori are of great interest. These are sketches that were to form the basis of an atlas of the Italian territory, which remains unfinished, that perfectly exemplify the interpretation of the territory that will be described in more detail in the following pages. Drawing 03-AC3 identifies the Hernici area between the Aniene valley floor to the north and the Sacco valley floor to the south, indicating the continuous counter-ridge connecting the low promontory settlements of Palestrina, Cave, Genazzano and Paliano; it identifies the formation of fabrics on the Hernici Mountain ridges; and it identifies the opposing continuous counter-ridge connecting Colleferro and Artena. Drawing 01-aC1 shows the study of the territorial organism of the Hernici area; formation of ridge routes with high and low promontory settlements;formation of the foothills; formation of the valley floor route along the Sacco corresponding to the route of Via Casilina with the settlements of Labico and Valmontone.
Drawing 15-AC15 provides a concise explanation of valley floor fabric formation as complementary to ridge fabrics in San Vito, Bellegra and Olevano. Lastly, Drawing 20-AC20 shows the identification of ridge routes converging towards the Hernici foothills between Palestrina and Cave, forming agricultural settlement fabrics separated by thalwegs.
In general, the formative process of these hierarchised cores, whose common characteristics are described, takes place in accordance with diachronic phases depending on the different relevant cultures. In the fourth century B.C., when Roman colonization and structuring or consolidation of the valley floor begins, the peninsula’s territory is still organized in proto-urban centres. Tribal settlements in central-southern Apennine inland areas consist in centres perched on headlands. While in Etruria, and along the central-south coastline, there is already a poelis system, city-states often indirectly influenced by Greek colonization.
Lastly, the coastal settlements are housing and commercial structures (corresponding to the market hubs that form at fords) which generate urban centres along the coast, often in relation to more inland low promontory settlements formed at the head of secondary ridges, with which trade is established. Moreover, the need for structured landing places with urban characteristics springs from the very necessity of trade, from the presence of a production area to be reached in the hinterland).
To conclude, it should be noted how the formative process of the route system and settlement system takes place within large time intervals that can be summarized, in brief, in the major cycles of the territory’s history.
The initial structure of the territory takes shape through the installation cycle dating from the Paleolithic to the fourth century A.D. starting from the mountain, as it has already been said, and running down to the valley, through routes and settlements.
With the consolidation cycle which can be dated as from Roman expansion of the fourth century B.C. to the fourth century A.D.. the already installed structure is consolidated, integrated by the planned structure of splitting of production areas, valley floor routes and relative urban centres.
The recovery cycle, identified in the medieval period between the end of the fourth century A.D. and the end of the twelfth century, marks, with the decline and disintegration of valley floor organised during the Roman period, the re-use of headland structures formed with the first cycle that are updated and expanded.
Lastly, during the reconstruction cycle that takes place in the period from the thirteenth century to the present, the valley floor structures, partially abandoned during the recovery cycle are reorganised with extensive land reclamation works.







